DENTAL EXAMS & CLEANINGS
DENTAL EXAMS & CLEANINGS
Dental Exam
Dental Exam
A comprehensive dental exam will be performed by your dentist at your initial dental visit.
At regular check-up exams, your dentist and hygienist will perform the following:
A comprehensive dental exam will be performed by your dentist at your initial dental visit. At regular check-up exams, your dentist and hygienist will perform the following:
Examination of diagnostic X-rays (radiographs): Essential for detection of decay, tumors, cysts, and bone loss. X-rays also help determine tooth and root positions.
Oral cancer screening: Check the face, neck, lips, tongue, throat, tissues, and gums for any signs of oral cancer.
Gum disease evaluation: Check the gums and bone around the teeth for any signs of periodontal disease.
Examination of tooth decay: All tooth surfaces will be checked for decay with special dental instruments.
Examination of existing restorations: Check current fillings, crowns, etc.
Examination of diagnostic X-rays (radiographs): Essential for detection of decay, tumors, cysts, and bone loss. X-rays also help determine tooth and root positions.
Oral cancer screening: Check the face, neck, lips, tongue, throat, tissues, and gums for any signs of oral cancer.
Gum disease evaluation: Check the gums and bone around the teeth for any signs of periodontal disease.
Examination of tooth decay: All tooth surfaces will be checked for decay with special dental instruments.
Examination of existing restorations: Check current fillings, crowns, etc.
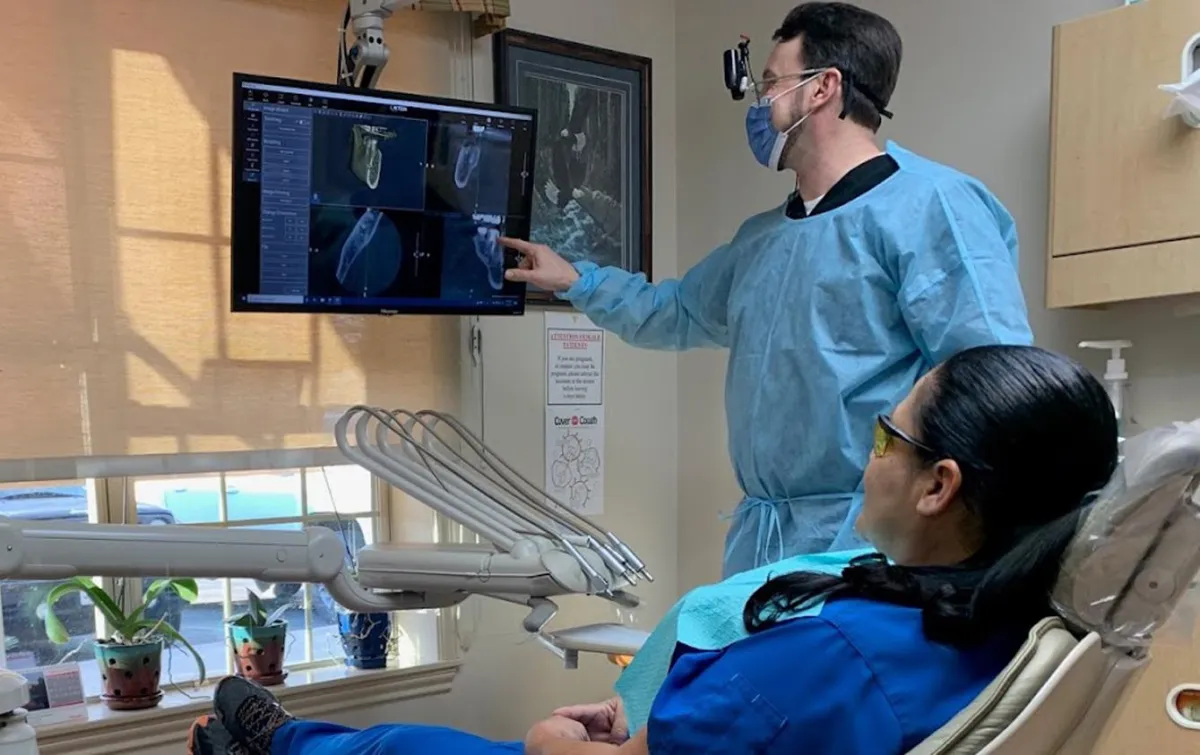
Professional Dental Cleaning
Professional Dental Cleaning
Professional dental cleanings (dental prophylaxis) are usually performed by Registered Dental Hygienists. Your cleaning appointment will include a dental exam and the following:
Professional dental cleanings (dental prophylaxis) are usually performed by Registered Dental Hygienists. Your cleaning appointment will include a dental exam and the following:
Bleeding gums– Gums should never bleed, even when you brush vigorously or use dental floss.
Loose teeth– Also caused by bone loss or weakened periodontal fibers (fibers that support the tooth to the bone).
New spacing between teeth– Caused by bone loss.
Persistent bad breath– Caused by bacteria in the mouth.
Pus around the teeth and gums– Sign that there is an infection present.
Receding gums– Loss of gum around a tooth.
Red and puffy gums– Gums should never be red or swollen.
Tenderness or Discomfort– Plaque, calculus, and bacteria irritate the gums and teeth.
Removal of calculus (tartar): Calculus is hardened plaque that has been left on the tooth for some time and is now firmly attached to the tooth surface. Calculus forms above and below the gum line and can only be removed with special dental instruments.
Removal of plaque: Plaque is a sticky, almost invisible film that forms on the teeth. It is a growing colony of living bacteria, food debris, and saliva. The bacteria produce toxins (poisons) that inflame the gums. This inflammation is the start of periodontal disease!
Teeth polishing: Remove stain and plaque that is not otherwise removed during tooth brushing and scaling.
Removal of calculus (tartar): Calculus is hardened plaque that has been left on the tooth for some time and is now firmly attached to the tooth surface. Calculus forms above and below the gum line and can only be removed with special dental instruments.
Removal of plaque: Plaque is a sticky, almost invisible film that forms on the teeth. It is a growing colony of living bacteria, food debris, and saliva. The bacteria produce toxins (poisons) that inflame the gums. This inflammation is the start of periodontal disease!
Teeth polishing: Remove stain and plaque that is not otherwise removed during tooth brushing and scaling.
RELATED PROCEDURES
RELATED PROCEDURES
What is Periodontal (Gum) Disease?
Diagnosis
Treatment
Maintenance
What is Periodontal (Gum) Disease?
Diagnosis
Treatment
Maintenance
RELATED PROCEDURES
Dental Exams & Cleanings
Dental X-rays
Home Care
How to Properly Brush & Floss
Schedule A Visit With Us Today!
Questions?
Give us a call today!
Address:
1313 Petersburg Street
Castroville, Texas 78009
Email:
Hours:
Monday - Thursday 8am to 5pm
Closed Friday - Sunday
© 2025. Medina Family Dental.
All Rights Reserved. Opt-In Form.


